ARPLANK Foam Plank Technical Guides, Specifications & Test Results
Read technical documents and compare specifications and test results to determine the best ARPLANK product for your application. If you have questions, contact ARPLANK Direct. Our staff are standing by to help you determine the perfect material for your project.
Design & Application Documents
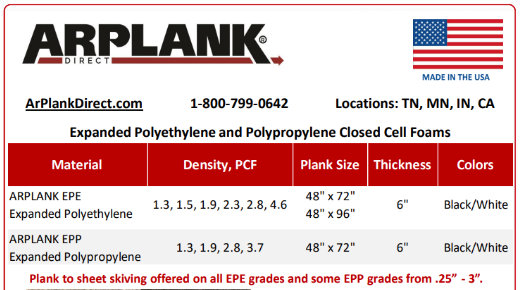
Arplank Direct Line Card
ARPLANK Direct supplies leading foam fabricators and manufacturers with high-quality expanded polyethylene (EPE) and expanded polypropylene (EPP) foam planks.
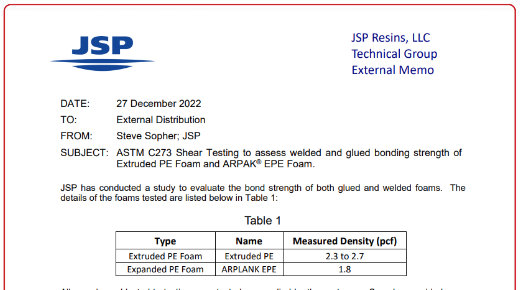
ASTM C273 Shear Testing to Assess Welded and Glued Bonding Strength of Extruded PE Foam and ARPAK® EPE Foam
JSP has conducted a study to evaluate the bond strength of both glued and welded foams
Foamed Product Carbon Footprint Study CO2(e) Comparison XLPE vs EPE
Recycled or Captured CO2 is used as a blowing agent to expand all ARPLANK EPE products.
Designing for Optimal Cushioning Performance with ARPRO EPP and ARPAK EPE
Packaging design is critical for package protection and cost control. Inadequate design results in shipping damage. Over design results in excessive packaging costs. This document will help you consider the basic packaging elements when using EPE and EPP foam materials. The easy interactive Design Worksheet on page 16 helps you manage and track your new design and re-design projects.
Applications for EPE & EPP Foams
EPE is a Class A surface and is low abrasion and highly resilient with excellent
multiple drop cushioning. EPP has high compressive strength with broad loading range, high energy absorption and service temperature.
Environmental Benefits of EPE & EPP Foams
ARPAK® Expanded Polyethylene (EPE) Products are produced using inert gas blowing agents. No VOCs are employed in the production of any ARPAK® EPE Products. ARPAK® EPE is the only product in the industry produced without a VOC blowing agent.
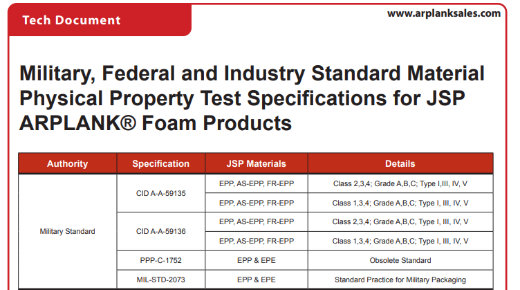
Technical Document: Military, Federal, and Industry Standard Test Specifications
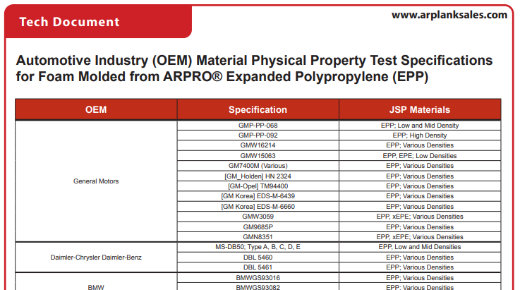
Automotive Industry (OEM) Material Physical Property Test Specifications for Foam Molded from ARPRO® Expanded Polypropylene (EPP)
Automotive Industry Standard Test Specifications
Military, Federal and Industry Standard Material Physical Property Test Specifications for Arplank materials.
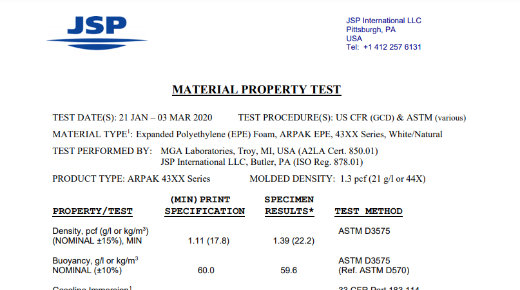
Technical Document: Coast Guard Flotation Material Property Test
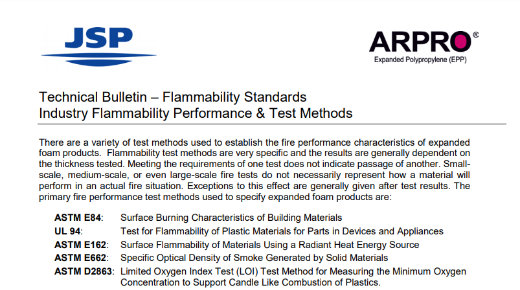
Technical Bulletin: Flammability Standards
There are a variety of test methods used to establish the fire performance characteristics of expanded foam products.
Physical Property Sheets
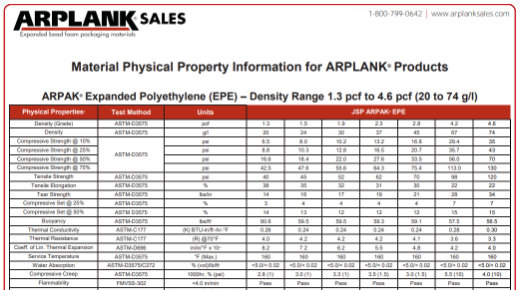
Physical Property Information: EPE
Material Physical Property Information for ARPLANK® ARPAK® Expanded Polyethylene (EPE) – Density Range 1.3 pcf to 4.6 pcf (20 to 74 g/l)
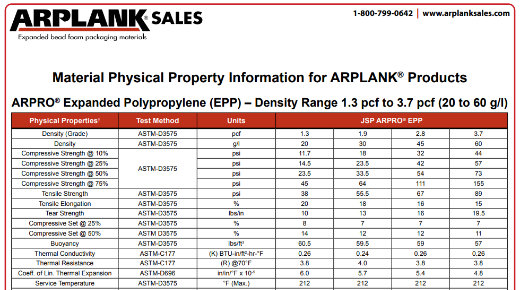
Physical Property Information: EPP
Material Physical Property Information for ARPLANK® ARPRO® Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) – Density Range 1.3 pcf to 3.7 pcf (20 to 60 g/l)
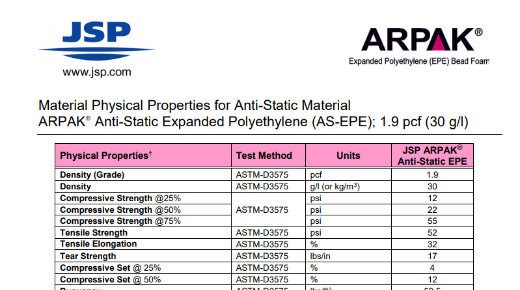
Physical Property Information: Anti-Static EPE
Material Physical Properties for Anti-Static Material – ARPAK Anti-Static Expanded Polyethylene (AS-EPE); 1.9 pcf (30 g/l)
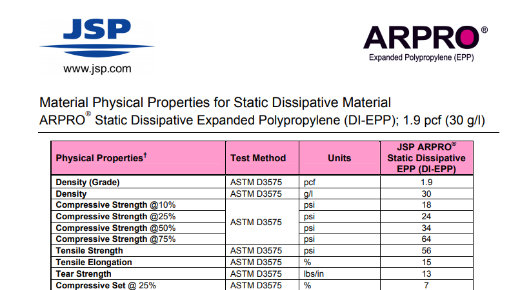
Physical Property Information: Anti-Static EPP
Material Physical Properties for Anti-Static Material ARPRO Anti-Static Expanded Polypropylene (AS-EPP)
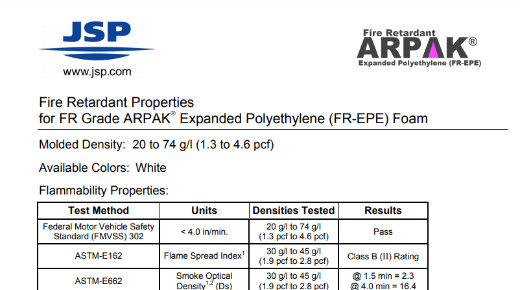
Physical Property Information: Fire Retardant (FR) EPE
Fire Retardant Properties for FR Grade ARPAK Expanded Polyethylene (FR-EPE Foam
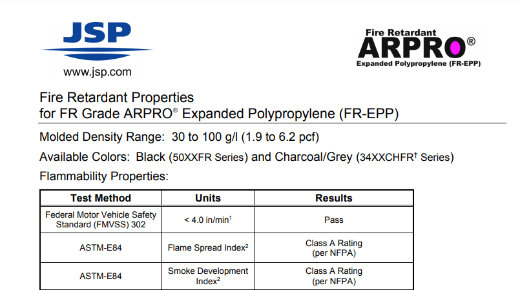
Physical Property Information: Fire Retardant (FR) EPP
Fire Retardant Properties for FR Grade ARPRO Expanded Polypropylene (FR-EPP) Foam
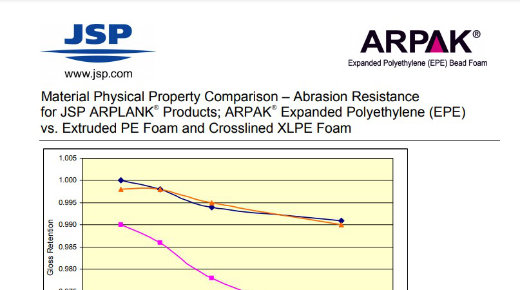
Technical Document: EPE Class A Surface Test
Abrasion Resistance for JSP ARPLANK® Products; ARPAK® Expanded Polyethylene (EPE) vs. Extruded PE Foam and Crosslinked XLPE Foam
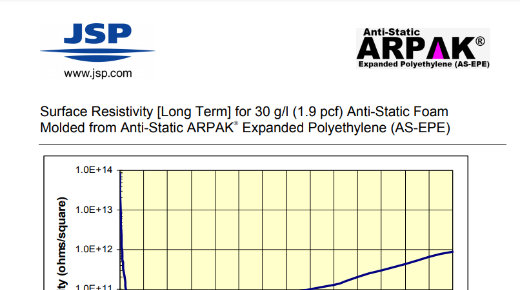
Technical Document: EPE Anti-Static Resistivity Test
Surface Resistivity [Long Term] for 30 g/l (1.9 pcf Anti-Static Foam Molded from Anti-Static ARPAK Expanded Polyethylene (AS-EPE)
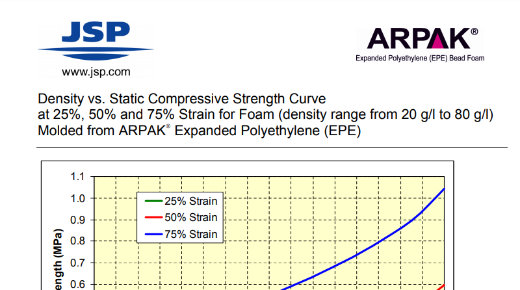
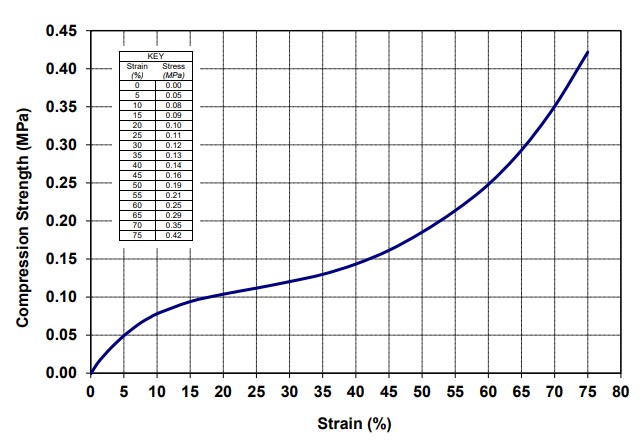
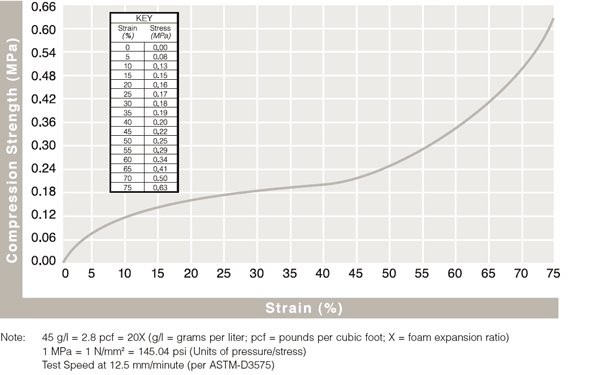
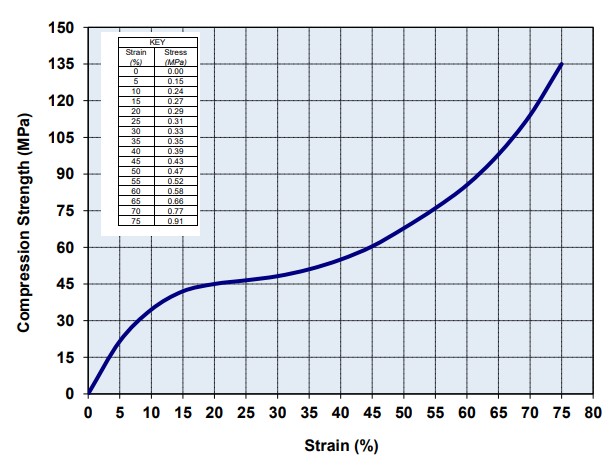
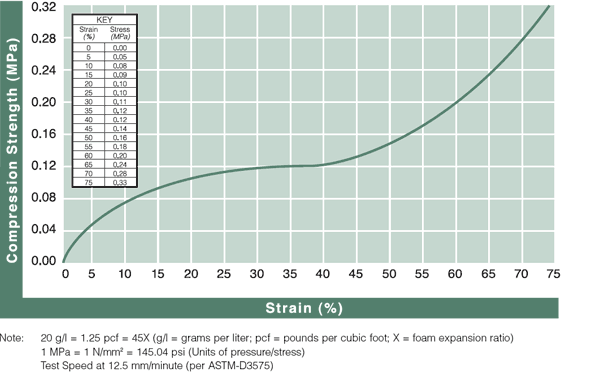
Technical Document: EPE Compressive Strength at 25%, 50%, and 75% Strain
Density vs. Static Compressive Strength Curve at 25%, 50%, and 75% Strain for Foam (density range from 20 g/l to 80 g/l)
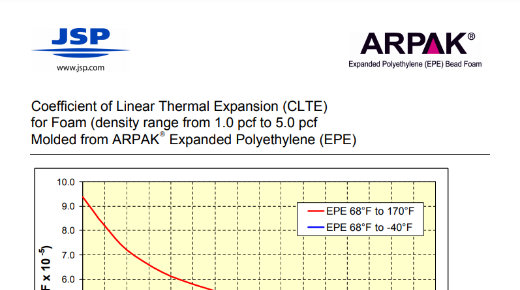
Technical Document: EPE Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion (CLTE)
CLTE for foam density range 1.0 pcf to 5.0 pcf molded from ARPAK® Expanded Polyethylene (EPE)
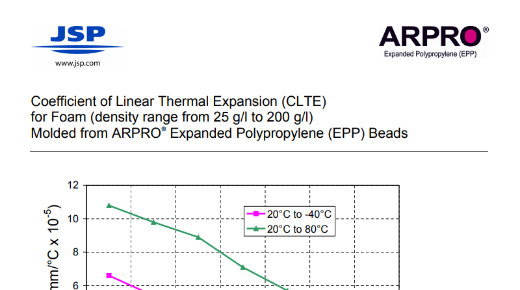
Technical Document: EPP Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion (CLTE)
CLTE for foam density range 25 g/l to 200 g/l molded from ARPRO® Expanded Polypropylene (EPP)
An Explanation of Foam Performance Test Methods
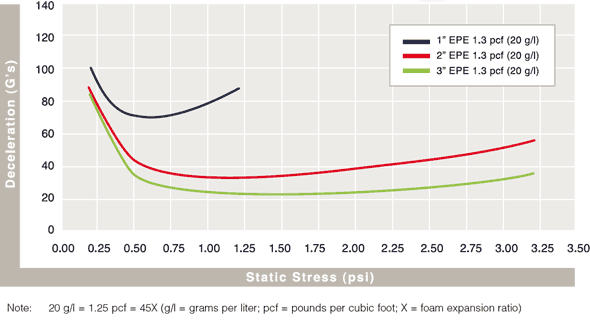
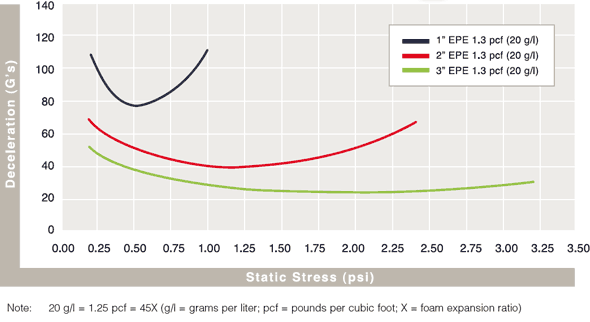
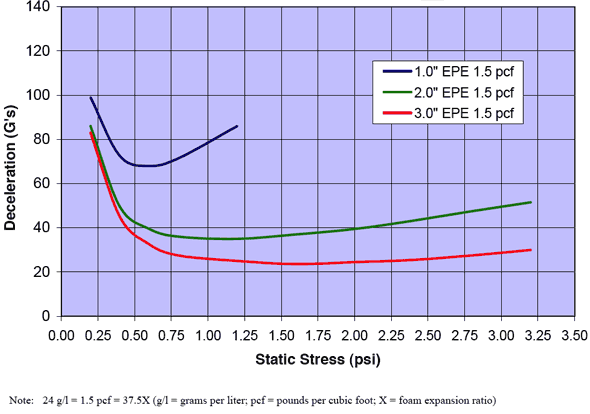
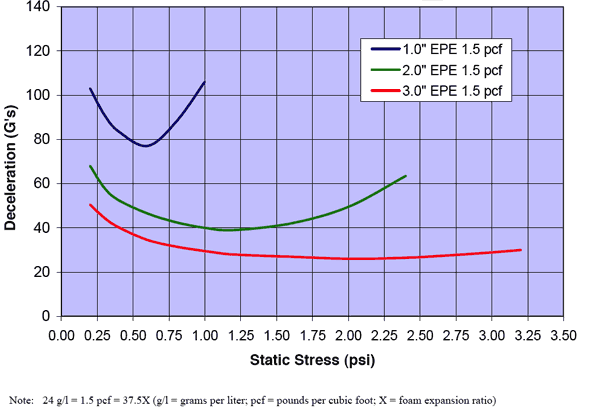
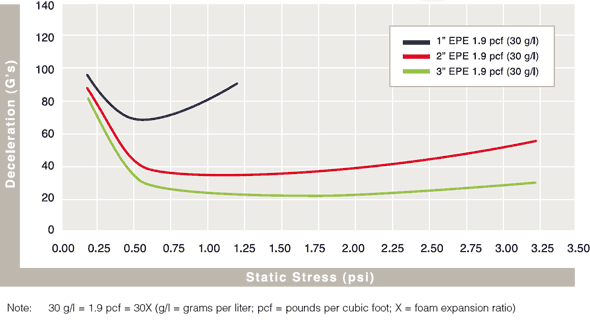
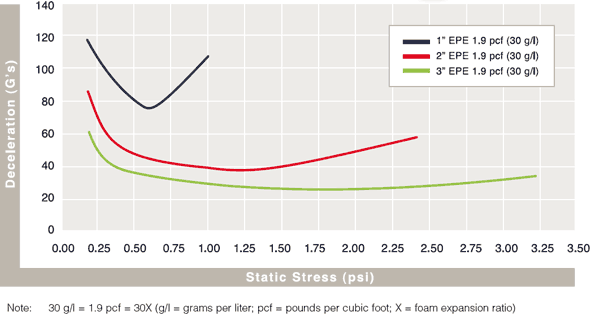
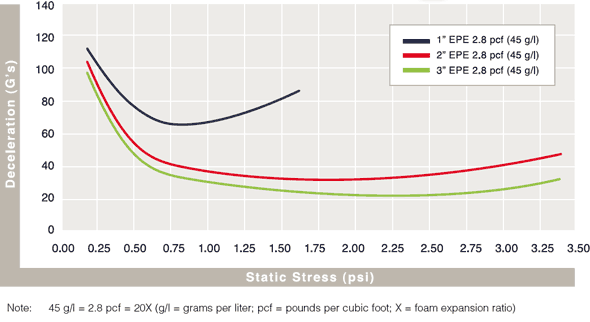
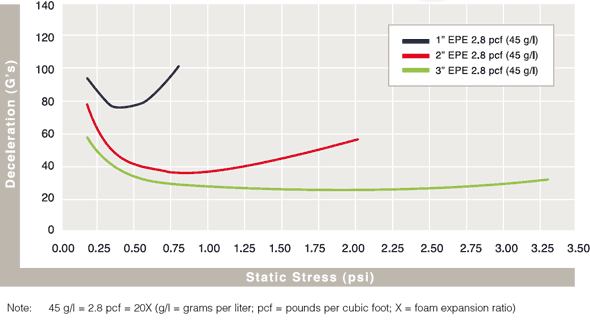
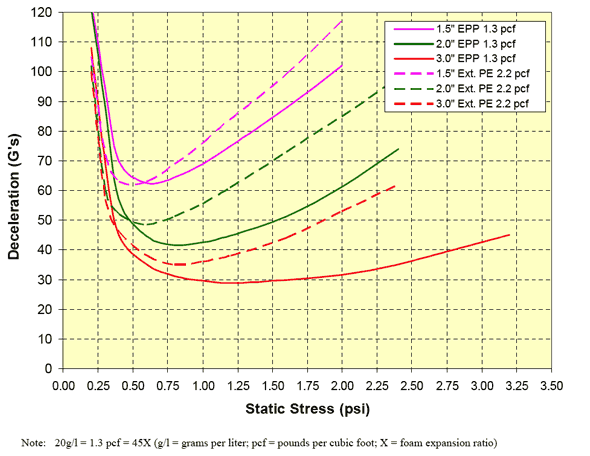
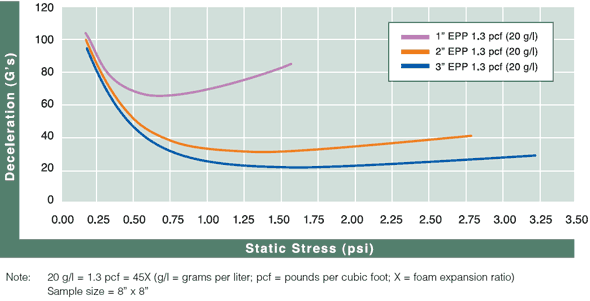
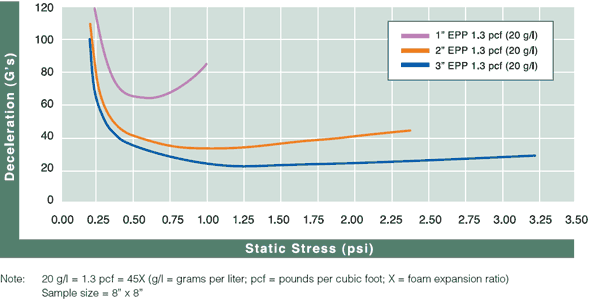
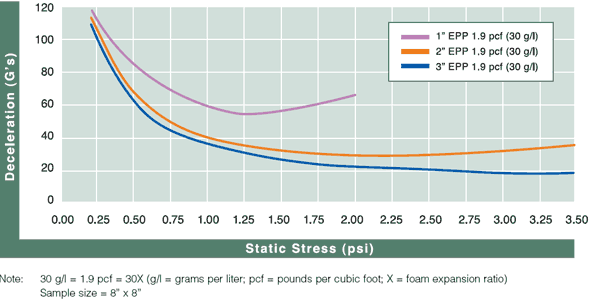
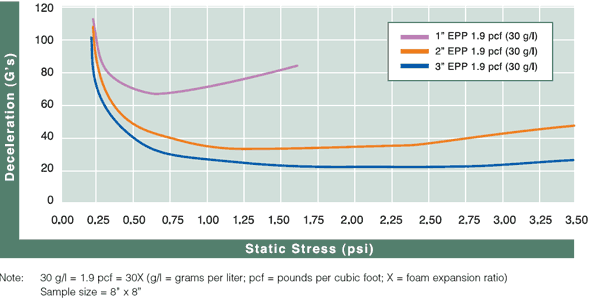
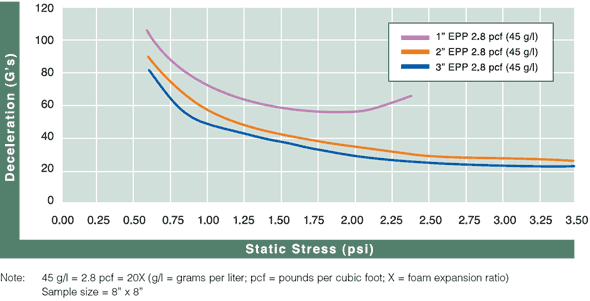
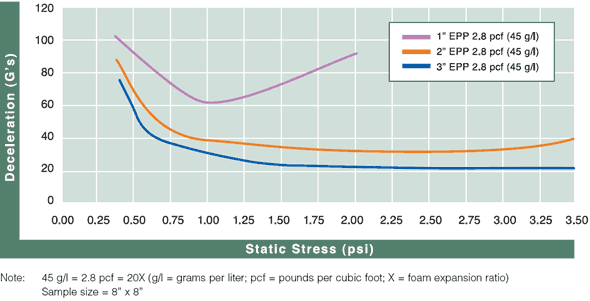
Cushion Curves
Cushion Curves represent the amount of shock or deceleration, commonly known as “G’s” that are transmitted through a cushion thickness when subject to specific load stresses. ARPLANK products are capable of managing the same amount of package protection with less foam material in many applications.
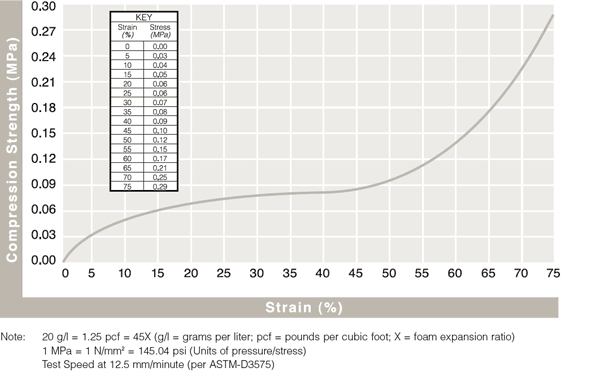
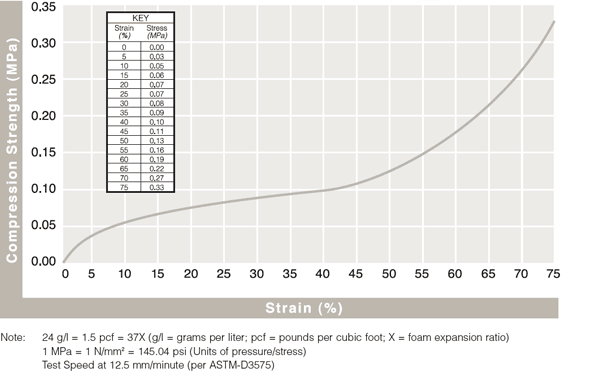
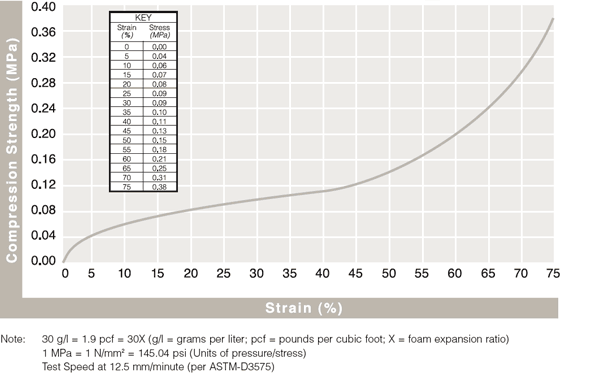
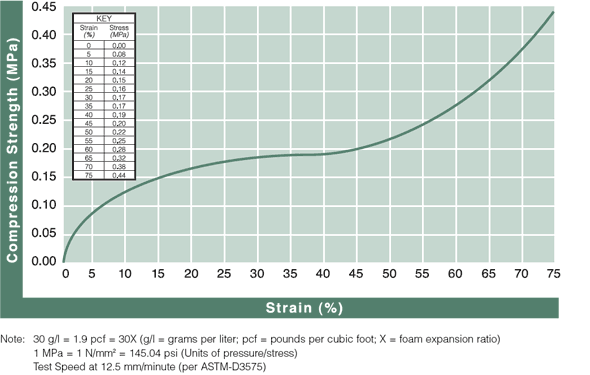
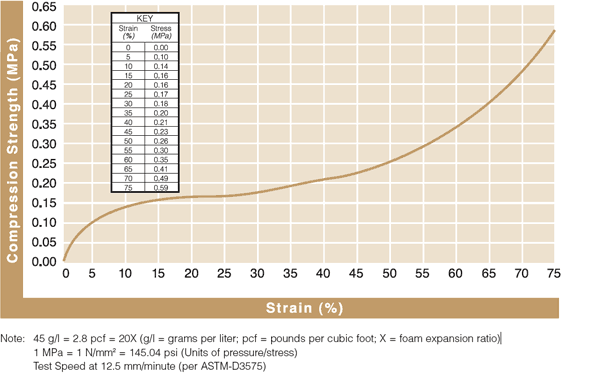
Static Compressive Strength Curves
Review results from ASTM-D3575 compression testing to see how ARPLANK expanded polyethylene and expanded polypropylene foam offer superior resilience and load bearing properties.
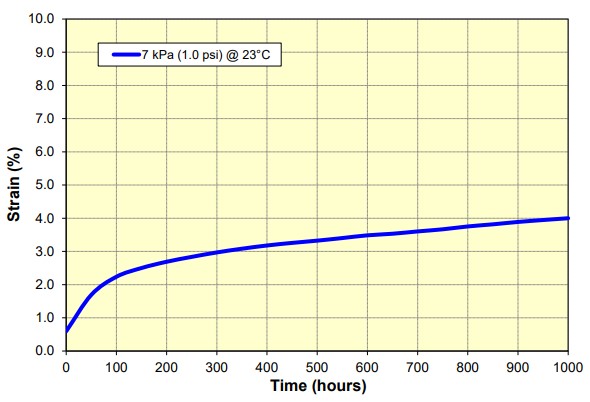
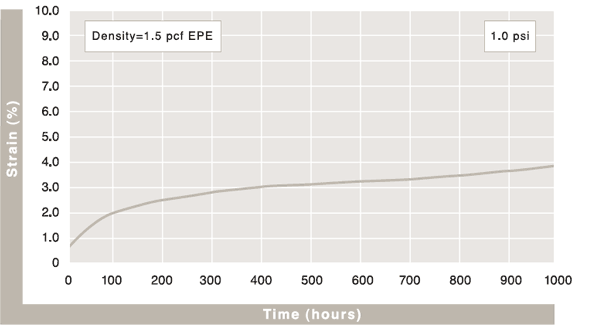
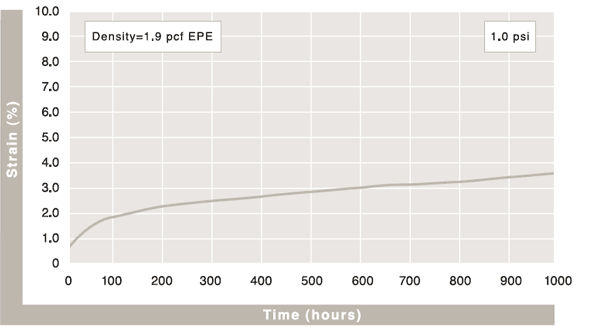
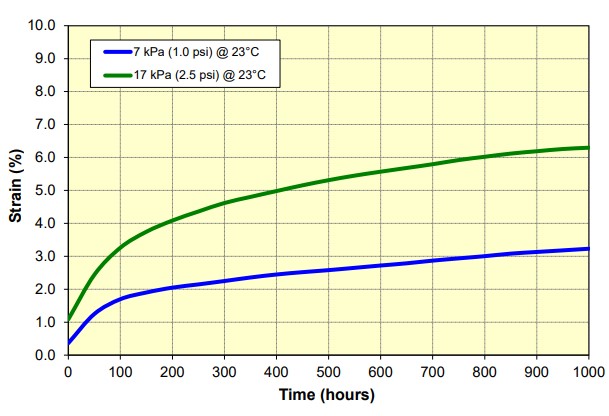
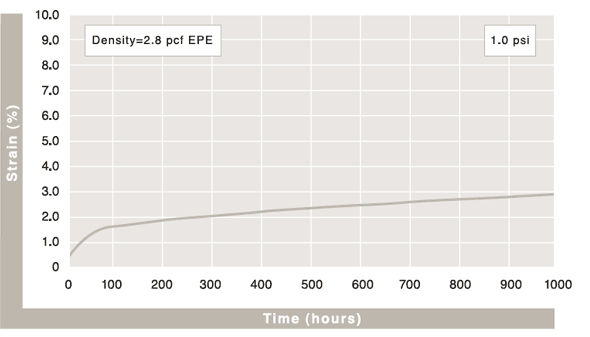
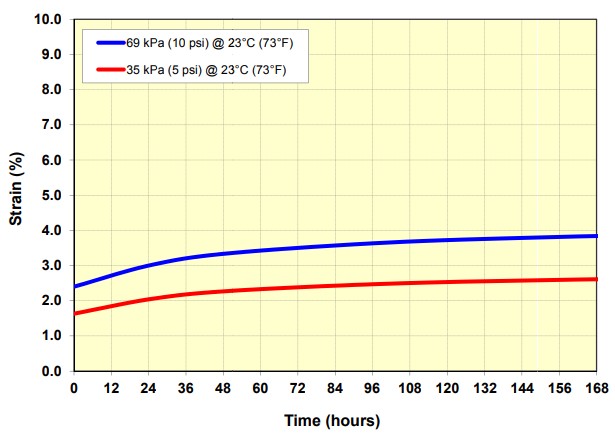
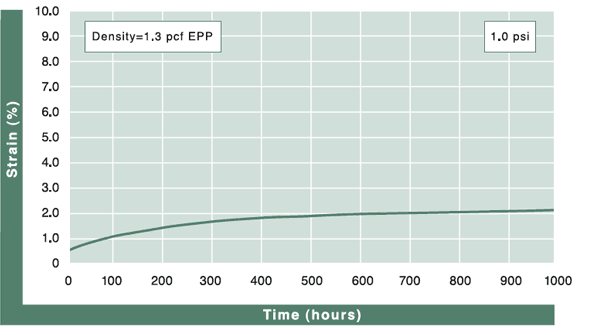
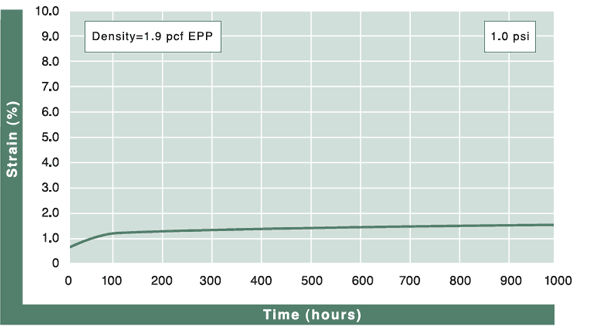
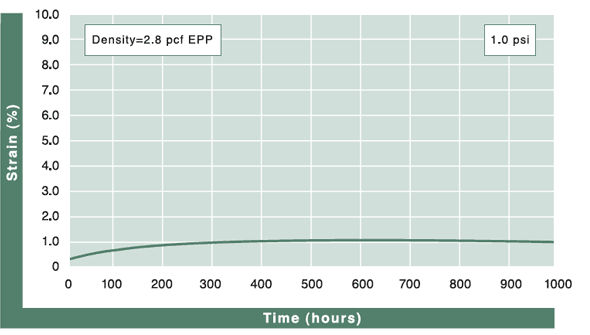
Compression Creep
The value representing the percentage of permanent foam height loss after being under specific loading, per ASTM-D3575. Beaded foam materials generally have less creep loss than other closed-cell foams because they are multi-directional in nature and can manage more surface bearing weight.
Vibration Response Data
Graphically shows how a package or container at a given frequency and cushion material will perform in a direct coupled, amplification, or attenuation vibration mode.
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
Complete physical data and material handling information for ARPLANK expanded polyethylene and expanded polypropylene foam planks.
ARPLANK Material Specifications Sheets
| Type | SCS | Cushioning Curves (1st drop) | Cushioning Curves (2nd-5th drop) | Compressive Strength | Compression Creep | Vibration Response | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPE | 1.3 pcf |  |  |  |  | ||
| EPE | 1.5 pcf |  |  |  |  | ||
| EPE | 1.9 pcf |  |  |  |  | ||
| EPE | 2.3 pcf |  |  |  | |||
| EPE | 2.8 pcf |  |  |  |  | ||
| EPE | 3.3 pcf | ||||||
| EPE | 4.6 pcf |  |  | ||||
| EPE | 1.3 pcf vs 2.2 Extruded PE |  | |||||
| EPP | 1.3 pcf |  |  |  |  | ||
| EPP | 1.3 pcf vs 2.2 Extruded PE |  | |||||
| EPP | 1.9 pcf |  |  |  |  | ||
| EPP | 2.8 pcf |  |  |  |  | ||
| EPP | 3.7 pcf |